Summary
MODSIM combines modeling and simulation into a single connected approach that improves how engineers explore ideas, validate decisions, and refine designs. This article introduces MODSIM in simple terms and explains what it is, why it matters, and what it helps engineers achieve. By looking at the fundamentals of the methodology and the workflow behind it, this article provides a clear starting point for anyone who wants to understand how unified design and simulation help modern engineering teams work more efficiently.
A Quick Introduction: What is MODSIM?
MODSIM stands for “Modeling and Simulation”. It describes a unified approach that brings design and simulation together so engineers can work within one continuous workflow. Instead of building a CAD model, sending it to a separate simulation tool, waiting for results, and then repeating the cycle, MODSIM connects everything from the beginning.
The main goal is simple. Engineers design and simulate as part of the same process, which helps them make better decisions earlier. This unified flow cuts down on rework because every change is supported by up-to-date simulation insights.
Many engineering teams still operate with disconnected design and analysis stages. MODSIM removes that separation. It places modeling and simulation into a single environment, so geometry, materials, loads, and performance data all come from the same source. This makes the engineering process clearer, faster, and easier to manage at scale.
Why was MODSIM Created?
For many years, design teams and simulation teams worked in separate spaces. This created several challenges that slowed down product development:
- Engineering changes often came after a design passed through multiple hands.
- Designs sometimes moved forward without enough early validation.
- Late-stage simulation revealed problems that were expensive to fix.
- CAD and CAE teams used separate tools that did not share information easily.
- Iteration cycles grew long, even when the required improvements were small.
MODSIM emerged to solve these issues by connecting design and analysis into one shared process. When simulation informs decisions during early design stages, engineers can explore more ideas without increasing the cost or time required to validate them. This approach reduces delays and supports better engineering outcomes.
The goal of MODSIM is not only to unify tools. It also aims to unify thinking by encouraging teams to treat simulation as part of design instead of a final check.
How does MODSIM Work in Practice?
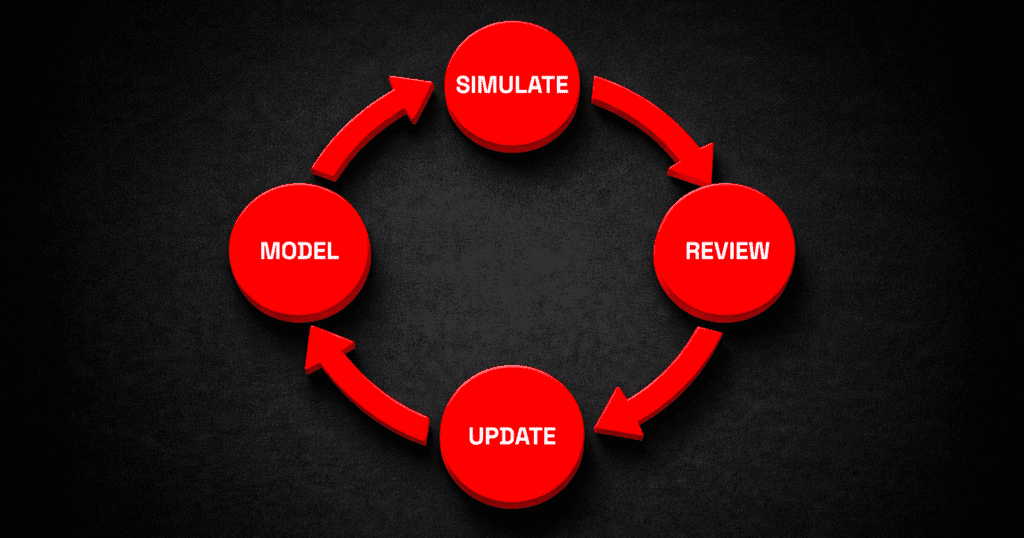
MODSIM creates a workflow where design and simulation rely on the same information. When engineers adjust a feature, update a constraint, or refine an assembly, the simulation setup stays connected. This avoids the usual problem where simulation models become out of sync with evolving CAD geometry.
A typical MODSIM workflow looks like this:
- The engineer creates or loads a model.
- Simulation parameters are applied directly to that model.
- The engineer evaluates the results and adjusts the design.
- The updated geometry automatically stays linked to the simulation study.
- The cycle repeats with less friction and fewer manual steps.
A unified approach makes it easier to test ideas rapidly. For example, if an engineer is shaping a bracket that needs to meet a specific stiffness requirement, they can adjust features and immediately see how those adjustments affect performance. This makes engineering feel more exploratory and less restricted by separate tool boundaries.
MODSIM also supports collaboration because every contributor works with consistent data. Design managers, simulation specialists, and manufacturing engineers can rely on the same model throughout the entire process.
Engineering Use Cases Where MODSIM Excels
MODSIM is helpful anywhere that performance, strength, or behavior matters. It is particularly useful in engineering tasks where early insights can prevent costly delays.
Lightweighting
Engineers test alternative geometries while shaping components for reduced weight. MODSIM helps them see how each design iteration affects performance before the part moves downstream.
Performance Optimization
When a design needs to meet specific performance targets, engineers can explore different configurations and study their impact without recreating or transferring data.
Early Validation
In many projects, early decisions determine later viability. MODSIM supports early design choices with accurate simulation insights.
Complex Assemblies
Large or multi-body designs benefit from unified workflows because changes in one area can influence performance across the entire system.
Safety or Failure Scenarios
Engineers can study load cases or failure modes during early development. This supports better planning and more robust design strategies.
Multi-Physics Studies
Some projects require more than structural analysis. With MODSIM, engineers can examine thermal, fluid, or dynamic behavior without managing separate versions of the same model.
These use cases show how MODSIM makes engineering more predictable and helps teams move from reactive problem-solving to proactive design exploration.
The Tools That Enable MODSIM
MODSIM is supported by platforms and tools designed to unify modeling and simulation. The 3DEXPERIENCE platform is a strong example of this because it brings design and analysis into one shared environment.
Modeling with CATIA
CATIA provides advanced modeling capabilities suited for complex geometries and assemblies. Engineers use it to create precise, well-structured models that form the foundation of MODSIM workflows.
Simulation with SIMULIA
SIMULIA delivers robust simulation tools that evaluate stiffness, strength, thermal behavior, motion, and fluid dynamics. It allows teams to understand how a design behaves in real-world conditions before building physical prototypes.
Connected Engineering on the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform links CATIA and SIMULIA so teams work with a single source of truth. Data stays synchronized, which avoids version conflicts and simplifies collaboration across teams. By using a platform that connects modeling and simulation, engineers achieve the unified workflow central to MODSIM.
Why MODSIM Matters for the Future of Engineering
Engineering teams are under pressure to produce better designs faster and with fewer physical prototypes. MODSIM helps teams meet these expectations by enabling faster validation, deeper exploration, and more informed decision-making.
A unified approach also supports sustainability because engineers can optimize designs earlier and reduce waste. It helps teams avoid rework, shorten development cycles, and gain confidence in their decisions before committing resources.
MODSIM also prepares organizations for broader shifts in digital engineering. The rise of virtual twins, connected data, and integrated workflows all rely on consistent, accurate models. MODSIM supports these initiatives by connecting design and analysis from the beginning.
Final Thoughts
MODSIM makes engineering more intuitive by treating modeling and simulation as one process. It offers a clear path for teams that want to improve their workflows, reduce iteration time, and explore ideas with confidence. By understanding the basics of MODSIM and how it connects design with simulation, engineers build a foundation for more advanced digital engineering practices.