Abstract
From the drawing board to the production line, 3D printing in automotive is changing how vehicles are designed, developed, and delivered. This article dives into the cutting-edge role of additive manufacturing in the industry, showing how it’s slashing development times, unlocking next-level customization, and driving more sustainable workflows.
Accelerating Innovation Through Rapid Prototyping
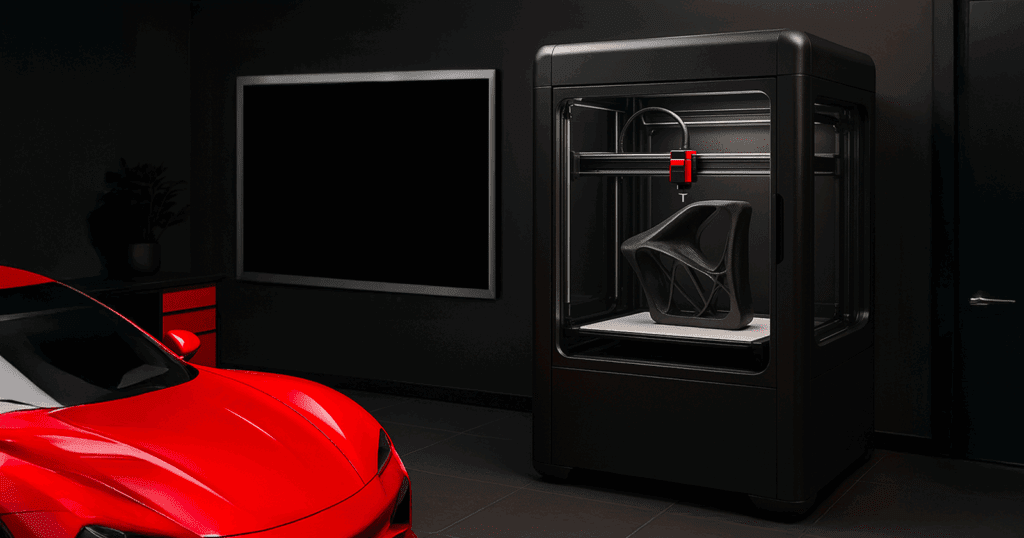
Prototyping is a vital stage in automotive design. Traditionally, creating physical prototypes was time-consuming and expensive. However, the use of 3D printing in automotive settings has transformed this process. Designers can now generate physical components within hours, iterate quickly, and make refinements with unparalleled flexibility.
This growing reliance on 3D printing in automotive workflows highlights its integral role in next-generation vehicle development.
As adoption increases, 3D printing in automotive will continue to unlock design freedom and production scalability.
The benefits of 3D printing in automotive prototyping are manifold: it reduces waste, saves time, and cuts costs. Engineers can experiment with bold, new ideas without being limited by tooling constraints. From ergonomic dashboard layouts to aerodynamic mirror housings, teams utilize 3D printing in automotive to visualize concepts and make data-driven decisions early in the design phase.
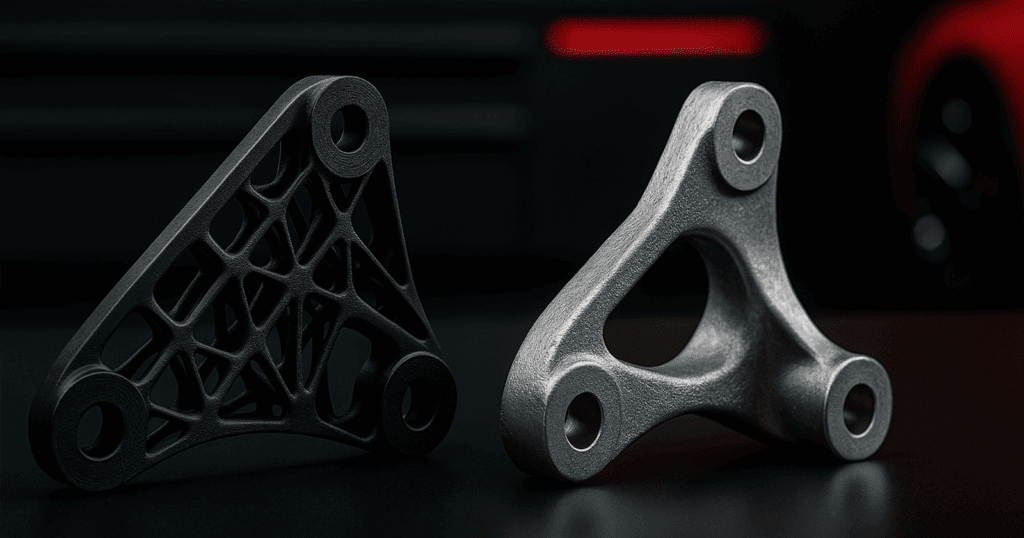
From Prototype to Production
While prototyping remains one of its core applications, 3D printing in automotive now plays an increasingly important role in producing functional parts. Additive manufacturing enables the creation of low-volume, end-use components that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to accommodate.
Innovations driven by 3D printing in automotive are transforming how manufacturers approach both design and production cycles.
Complex geometries, such as custom HVAC vents, lattice structures, or lightweight seat brackets, are easily fabricated with 3D printing in automotive production workflows.
These components aren’t just conceptual—they’re being installed in test vehicles and limited-run models, proving the viability of 3D printed parts in real-world applications.
Enhancing Customization and Personalization
Today’s drivers want more than just reliable vehicles—they want options tailored to their preferences. 3D printing in automotive empowers manufacturers to deliver on these expectations without the high costs associated with retooling production lines.
From custom gear shifts and control panels to personalized door trims and branding details, 3D printing in automotive environments supports small-batch and one-off manufacturing.
Smarter Tooling and Manufacturing Aids
Beyond vehicle components, 3D printing in automotive also enhances efficiency behind the scenes. Automotive manufacturers use it to produce jigs, fixtures, and tooling customized to their assembly processes. These tools can be designed, printed, and deployed in a matter of days—streamlining workflows and reducing downtime.
The result is a more agile production line, where updates and improvements can be implemented rapidly. In this context, 3D printing in automotive supports not just product innovation but also smarter manufacturing strategies.
Integrated Digital Workflows
As automotive development becomes increasingly digital, 3D printing in automotive integrates seamlessly with CAD and simulation environments. Engineers can design parts, validate them virtually, and push print-ready files directly to additive machines.
This digital thread enhances collaboration among teams and shortens time-to-market. In many projects, 3D printing in automotive bridges the gap between virtual simulation and physical testing—offering a feedback loop that accelerates improvement.
Advancing Sustainability Goals
Sustainability is no longer optional—it’s a business imperative. 3D printing in automotive contributes to greener production through material efficiency, localized manufacturing, and reduced inventory needs. Because components are produced on demand, there is less waste and fewer emissions associated with transportation and storage.
Moreover, 3D printing in automotive applications increasingly use recyclable and bio-based materials, aligning with the industry’s environmental objectives. By adopting additive methods, automakers are advancing both technological and ecological innovation.
Real-World Applications: Where Innovation Meets the Road
Automotive companies worldwide are embracing 3D printing in automotive to stay ahead. From high-performance sports cars to utilitarian EVs, the technology is proving its versatility. Race teams use 3D printing in automotive to fabricate aerodynamic parts on short notice. Startups use it to build proof-of-concept vehicles without investing in tooling. Established brands turn to 3D printing in automotive for spare parts, trim upgrades, and factory optimizations.
The adaptability of 3D printing in automotive workflows means it can be scaled across departments—from R&D to aftermarket services—allowing manufacturers to experiment, produce, and refine with minimal barriers.
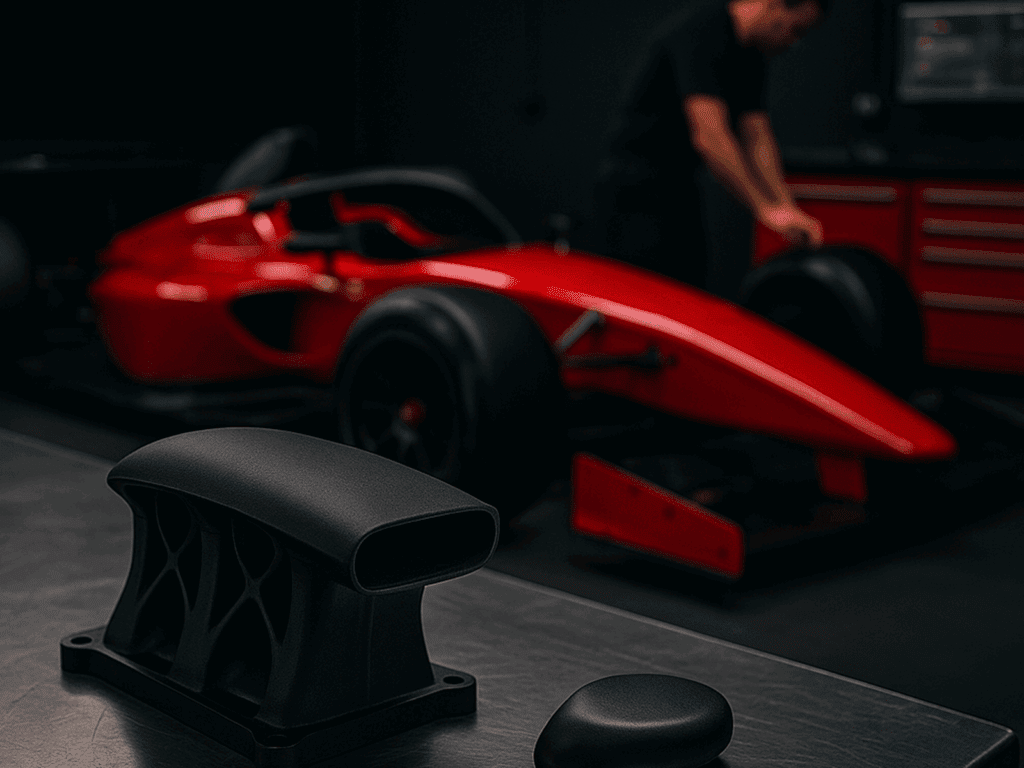
meta: A matte black 3D-printed air intake manifold and a custom gear knob rest on a metal workbench in a dimly lit racing garage. In the background, a red Formula-style sports car is being fine-tuned by a technician, reflecting the use of 3D printing in high-performance and aftermarket automotive contexts.
One area where 3D printing in automotive continues to gain traction is in the aftermarket and motorsports sectors. Custom performance parts, aerodynamic enhancements, and even cosmetic upgrades are being tailored using 3D printing technologies. In motorsports, where every millisecond matters, teams rely on the speed and flexibility of 3D printing in automotive contexts to prototype and produce components that respond to unique track conditions or driver preferences. This flexibility allows for rapid adaptation between races, ensuring that vehicle performance remains optimal. Furthermore, aftermarket suppliers benefit from the ability to meet niche demands without investing heavily in tooling or mass production runs. Enthusiasts can order personalized parts that match their style or performance needs, whether it’s a lightweight air intake manifold, a customized exhaust bracket, or a one-of-a-kind gear knob. The expanding use of 3D printing in automotive aftermarket applications underscores how versatile and accessible the technology has become—not just for major manufacturers, but for smaller players and individual users alike. This democratization of innovation is helping to reshape expectations about what’s possible in vehicle design and ownership.
Conclusion: The Road Ahead
The impact of 3D printing in automotive design is profound. As the industry navigates the challenges of electrification, personalization, and sustainability, additive manufacturing provides a toolkit for solving problems creatively and cost-effectively.
Whether you’re a startup pushing boundaries or a global OEM rethinking production, 3D printing in automotive offers agility, innovation, and resilience. The road ahead will be shaped by companies that embrace these tools—not just to keep pace, but to lead the way.
Ready to embrace the future of automotive design? Contact Mecanica today to explore tailored solutions that bring the benefits of 3D printing in automotive directly to your engineering floor.